GPS tracker for car provides real-time location tracking, geofencing, and vehicle speed monitoring, making it a valuable tool for fleet management and personal use. Understanding the diverse types, features, and applications of these devices is key to choosing the right one for your needs.
This guide delves into the various aspects of GPS car tracking, from installation and setup to security and privacy considerations, and finally, future trends in this evolving technology. We’ll explore the benefits and applications of GPS tracking for both businesses and individuals, offering insights into optimizing logistics and improving safety.
Features and Functionalities of GPS Car Trackers
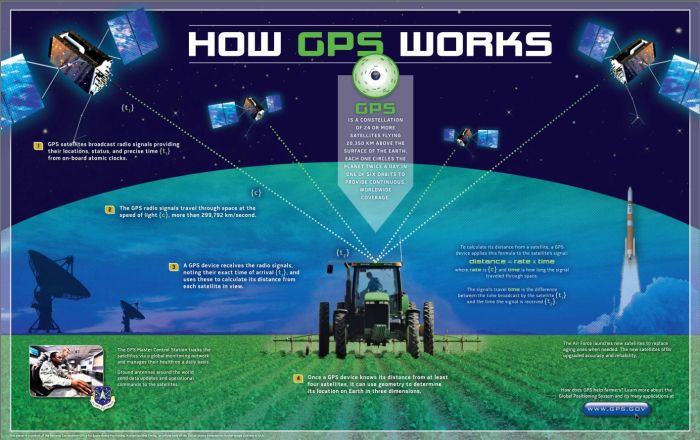
Modern GPS trackers for vehicles offer a wealth of functionalities beyond basic location tracking. These devices are becoming increasingly sophisticated, providing valuable data for fleet management, driver safety, and vehicle maintenance. This detailed exploration delves into the core features and functionalities, showcasing the capabilities of modern GPS car trackers.Real-time location tracking is a fundamental feature of most GPS trackers.
This functionality allows for continuous monitoring of a vehicle’s position, providing immediate updates on its whereabouts. This is crucial for fleet management, enabling real-time visibility of vehicle movements and ensuring efficient routing and scheduling. For example, a delivery company can track the location of its trucks in real-time, allowing for better delivery scheduling and optimization of routes.
Real-Time Location Tracking
Real-time tracking allows for instant updates on the vehicle’s position, enabling immediate responses to potential issues. This feature is vital for fleet management, providing constant visibility of vehicle movements. The data is often presented on a map interface, allowing for easy visualization and interpretation.
Geofencing
Geofencing is a powerful feature enabling alerts when a vehicle enters or exits a predefined geographical area. This is particularly useful for security and asset management. For example, a business can set up geofences around their warehouse or sensitive locations, triggering alerts if a vehicle enters or leaves those areas outside of designated hours. This functionality helps prevent unauthorized vehicle movement and enhances security.
Vehicle Speed Monitoring
Vehicle speed monitoring is an important feature for safety and compliance. GPS trackers can record and report vehicle speed data, helping to ensure that speed limits are adhered to. This data can be used to identify potential safety risks or driver behavior issues. This is particularly important for businesses with multiple vehicles, enabling the monitoring of speed and the detection of potential violations.
Data Collection
GPS trackers collect various data points, offering a comprehensive view of vehicle activity. This data includes location history, speed, engine status, and fuel consumption (in some models). The collected data can be used to optimize routes, monitor driver behavior, and predict maintenance needs. This wealth of data allows for proactive decision-making regarding vehicle operations.
Location History
The location history feature records the vehicle’s position over a specific period, providing a detailed record of its movement. This is invaluable for auditing purposes, enabling businesses to track the vehicle’s journey for compliance or other reasons. The historical data can be analyzed to identify patterns or trends in vehicle usage.
Engine Status
Engine status data provides insights into the vehicle’s operational health. Data on engine start and stop times, along with other relevant indicators, can assist in identifying potential mechanical issues or maintenance needs. This information can help prevent costly repairs by enabling proactive maintenance schedules.
Advanced Functionalities
Advanced GPS trackers often incorporate additional functionalities to enhance their utility. These include automatic incident detection and driver behavior analysis. This advanced capability is a significant enhancement, improving the overall safety and efficiency of vehicle operations.
Automatic Incident Detection
Automatic incident detection utilizes various sensors and algorithms to identify potential incidents such as accidents, collisions, or vehicle theft. This feature can automatically alert authorities or designated personnel, enabling swift responses and preventing further harm or damage. This is a significant safety feature, especially for fleets operating in challenging or remote areas.
Driver Behavior Analysis
Driver behavior analysis uses data collected by GPS trackers to evaluate driver performance and identify potential safety concerns. This includes monitoring acceleration, braking, and harsh cornering, providing insights into driving styles and potential risks. This data can help businesses improve driver training and reduce accidents. It also helps to identify drivers who may need additional training or support to enhance their driving skills.
Vehicle Maintenance Optimization
The collected data can significantly aid in optimizing vehicle maintenance schedules. Analyzing patterns in vehicle usage and speed data can predict maintenance needs, enabling businesses to schedule repairs proactively. This approach reduces downtime and minimizes unexpected repairs. This data analysis allows for more effective scheduling of maintenance tasks, preventing costly breakdowns and minimizing downtime.
Installation and Setup Procedures
Proper installation and setup of a GPS tracker are crucial for ensuring reliable vehicle monitoring and optimal performance. Incorrect installation can lead to inaccurate tracking data and potential malfunctions. Following the detailed procedures Artikeld below will guarantee a smooth and effective installation process.The setup process varies slightly depending on the specific GPS tracker model and the vehicle type.
However, common steps like device mounting, wiring, and software configuration remain consistent across different GPS trackers. Thorough adherence to these instructions is essential for seamless integration and reliable tracking functionality.
Hardware Requirements
A comprehensive list of the necessary hardware components for installation is presented below. These components ensure a successful installation and proper functionality.
- GPS Tracker Device: The core component of the system, ensuring accurate location data and communication with the monitoring platform.
- Power Supply: A reliable power source to keep the GPS tracker functioning, typically a vehicle’s 12-volt power system. Appropriate cabling is vital for safe connection.
- Mounting Hardware: This includes adhesive mounts, suction cups, or brackets, depending on the chosen installation method and the GPS tracker’s design. The mount should be sturdy and securely attach to the vehicle’s interior or exterior.
- Wiring Harness: Necessary for connecting the GPS tracker to the vehicle’s electrical system. Ensure correct polarity and amperage ratings to avoid damage to the tracker or vehicle.
Software Requirements
The software requirements for proper operation of the GPS tracker system include the monitoring platform’s software. A compatible mobile application or web portal is required to access and interpret the tracked data.
- Monitoring Platform Software: A dedicated software application or web portal is essential for accessing and analyzing the GPS tracker’s data. This allows for real-time tracking, historical data review, and geofencing features.
- Compatible Device: A mobile device or computer with a stable internet connection is needed for accessing the monitoring platform. A reliable internet connection is necessary to receive and transmit data efficiently.
Installation Methods, GPS tracker for car
Different installation methods cater to various vehicle types and GPS tracker models. Careful consideration of the chosen method is critical for achieving secure and effective integration.
- Dashboard Mounting: Suitable for vehicles with flat dashboards, this method involves using a suction cup or adhesive mount to securely position the GPS tracker on the dashboard. This method is often preferred for its ease of access and visibility.
- Under-the-Dashboard Mounting: Suitable for vehicles with limited dashboard space or where a dashboard mount is not ideal. The GPS tracker is placed under the dashboard, often using adhesive mounts or brackets, to minimize visibility and potential interference.
- Windshield Mounting: An effective method for vehicles that require a visible GPS tracker. This method utilizes a suction cup or adhesive mount on the windshield for optimal visibility.
Configuration and Activation
The configuration and activation steps are crucial for the GPS tracker’s operational efficiency. Correct configuration ensures accurate data transmission and reliable monitoring.
- Power Connection: Connect the GPS tracker’s power cable to the vehicle’s 12-volt power source. Ensure proper polarity to prevent damage to the device.
- Software Configuration: Access the monitoring platform’s software and configure the GPS tracker’s settings, such as device name, geofencing boundaries, and notification parameters. This step allows customization for specific needs.
- Activation Process: Follow the instructions provided by the GPS tracker manufacturer to activate the device. Activation typically involves entering a unique code or completing a series of prompts on the monitoring platform.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Protecting user data and maintaining privacy are paramount when deploying GPS tracking devices. These considerations extend beyond the technical aspects of the device to encompass legal and regulatory frameworks. A robust security approach is essential to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the collected data.
Data Encryption and Secure Transmission Protocols
Data encryption is a crucial element in safeguarding sensitive information transmitted by GPS trackers. Modern GPS trackers employ encryption algorithms to scramble data, rendering it unreadable to unauthorized parties. This ensures that even if intercepted, the data remains unintelligible without the appropriate decryption key. Secure transmission protocols, such as TLS/SSL, are vital to encrypt communications between the tracker and the receiving platform.
This encrypted communication channel prevents eavesdropping and tampering with the data stream.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects of GPS Tracking
Navigating the legal and regulatory landscape surrounding GPS tracking is essential for responsible deployment. Different jurisdictions have varying regulations concerning the use of GPS trackers, especially in relation to individuals. Compliance with these regulations is critical to avoid legal repercussions. This includes obtaining informed consent from the vehicle owner or user. Additionally, data retention policies and disposal procedures must align with local laws.
Potential Security Risks and Vulnerabilities
Several potential security risks and vulnerabilities need consideration when implementing GPS tracking systems. These vulnerabilities can arise from various sources, including hardware flaws, software bugs, and network vulnerabilities. The security of the GPS tracker’s hardware and software components is critical. Weak passwords or insecure configurations of the tracking system can expose it to hacking attempts. Robust security measures are required to protect against unauthorized access to the tracker and the data it collects.
Furthermore, potential denial-of-service attacks targeting the communication network or the central server hosting the data can disrupt the functionality of the system. The risk of physical tampering with the tracker, such as disabling or altering the device, also needs to be considered.
Integration with Other Systems

GPS car trackers offer a versatile platform for integrating with existing vehicle management systems. This seamless integration allows for a more comprehensive understanding of vehicle operations, enhancing efficiency and productivity. This integration often results in a unified view of vehicle data, enabling businesses to make informed decisions regarding fleet management, logistics, and safety.
Integration with Vehicle Management Systems
Vehicle management systems (VMS) often encompass a wide range of functionalities, including tracking, maintenance scheduling, driver performance monitoring, and fuel consumption analysis. GPS trackers seamlessly integrate with these systems, providing real-time location data and enriching the existing data pool. This integration streamlines data collection and analysis, offering a holistic view of fleet operations. The result is a powerful tool for optimizing operational efficiency.
Integration with Fleet Management Software
GPS tracking data directly enhances fleet management software. This integration empowers businesses to gain insights into driver behavior, vehicle maintenance needs, and overall operational efficiency. Real-time location data, combined with other parameters like speed and idling time, helps identify areas for improvement in fleet management.
Integration with Mobile Apps and Web Dashboards
GPS tracking systems can be integrated with intuitive mobile applications and web dashboards. These user-friendly interfaces allow for real-time monitoring of vehicle locations, providing valuable insights to fleet managers and dispatchers. Real-time data access fosters proactive decision-making, enabling businesses to respond quickly to potential issues or optimize routes in real-time.
Optimization of Logistics and Delivery Routes
GPS tracking data plays a pivotal role in optimizing logistics and delivery routes. Real-time location information allows for dynamic route adjustments, reducing travel time and fuel consumption. This real-time adjustment is possible due to the flexibility of the data and the real-time access to it. Furthermore, GPS data enables better estimations of delivery times, enhancing customer satisfaction and improving overall operational efficiency.
A prime example is a courier service optimizing its delivery routes using real-time traffic data to arrive at destinations on time. By incorporating GPS data into their fleet management system, they can dynamically adjust routes, avoiding congestion and improving delivery times.
Data Visualization and Reporting
Effective data visualization is crucial for extracting actionable insights from GPS tracker data. Clear and concise representations of vehicle location, speed, and travel patterns empower users to optimize routes, manage resources, and identify potential issues promptly. This section details how GPS tracking data is visualized and reported, including typical displays and generated reports.
Typical GPS Tracker Data Visualizations
Real-time location plots, speed charts, and trip summaries are common visualizations in GPS tracking systems. These visualizations provide a clear and dynamic picture of vehicle movement, enabling users to monitor vehicles in real-time and understand their operational patterns.
- Real-time location plots: These dynamic maps display the current location of tracked vehicles. They typically use interactive features like zooming, panning, and marker highlighting to aid in navigating and identifying vehicles on the map. Real-time updates ensure the plots reflect the vehicles’ precise position at any given moment.
- Speed charts: These charts visually represent the speed of a vehicle over time. They can be categorized by specific trips, timeframes, or individual vehicles. These charts help users monitor adherence to speed limits and identify instances of unusual acceleration or deceleration.
- Trip summaries: These reports provide detailed information about each trip, including start and end times, duration, total distance covered, average speed, and maximum speed. Trip summaries are invaluable for optimizing routes and identifying any anomalies in vehicle usage patterns. For instance, a sudden spike in average speed might indicate an emergency situation or an unauthorized deviation from the planned route.
Data Presentation Methods
Various methods can be employed to effectively display vehicle location tracking data. Maps and graphs are crucial tools for understanding vehicle movement and patterns.
- Maps: Interactive maps provide a spatial context for vehicle locations. Users can overlay different data layers on the map, such as speed, routes, or areas of interest, enabling a comprehensive view of vehicle activity. The user can filter, zoom, and pan to focus on specific regions or time periods, making it easier to understand vehicle movements.
- Graphs: Graphs are useful for visualizing trends and patterns in vehicle data. For instance, a line graph can show the speed of a vehicle over time, highlighting potential irregularities. Bar charts can compare the total distance traveled by different vehicles or routes.
Examples of Generated Reports
GPS tracking data can generate various reports, offering insights into operational efficiency and potential issues.
| Report Type | Key Insights | Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Daily Trip Summary | Identifies the most frequent routes, total distances traveled, and average speeds for each day. | Total distance, average speed, duration of each trip, start/end locations |
| Vehicle Performance Report | Highlights vehicle usage patterns, identifies potential maintenance issues, and tracks fuel efficiency. | Fuel consumption, idling time, maximum/minimum speed, acceleration/deceleration patterns |
| Deviation Report | Flags instances where a vehicle deviated from the planned route, providing information about the deviation and duration. | Deviation duration, distance deviated, reason for deviation (if available), location of deviation |
Data Display Format
A structured format is essential for displaying GPS tracker data effectively. Tables can efficiently present data points, enabling users to quickly access specific information. Examples include timestamps, locations (latitude/longitude), speed, and other relevant data points.
Data points are crucial for comprehensive analysis and reporting. They form the foundation for understanding vehicle movement and operational patterns.
Benefits and Applications of GPS Tracking
GPS tracking offers a powerful suite of advantages for various applications, ranging from optimizing fleet management to enhancing personal safety. By leveraging real-time location data, businesses and individuals can streamline operations, improve decision-making, and enhance overall efficiency. This technology provides valuable insights into movements and activities, enabling proactive measures and cost savings.GPS tracking systems provide precise location data, enabling businesses to monitor assets, vehicles, and personnel.
This real-time visibility fosters better control over operations, reduces risks, and ultimately drives greater profitability.
Fleet Management Benefits
Real-time tracking of vehicles significantly improves fleet management. This leads to enhanced operational efficiency and cost reduction through optimized routes, reduced fuel consumption, and minimized downtime. Predictive maintenance is also facilitated, allowing proactive interventions and preventing costly breakdowns.
- Optimized Routes and Fuel Efficiency: GPS tracking allows for the identification of the most efficient routes, leading to optimized fuel consumption and reduced operating costs. For example, a company using GPS tracking for its delivery trucks might discover that using alternative routes, avoiding traffic congestion, or consolidating deliveries can save significant amounts of fuel, reducing overall operational costs and environmental impact.
- Reduced Downtime and Maintenance Costs: Tracking enables the identification of potential issues with vehicles early on. This allows for proactive maintenance schedules, reducing unplanned downtime and associated costs. For instance, a fleet manager can schedule maintenance based on usage patterns and mileage, rather than relying on fixed intervals. This preventive approach significantly lowers maintenance expenses.
- Improved Driver Performance: GPS tracking data can provide insights into driver behavior, such as speeding, harsh braking, and idling time. This information can be used to improve driver training programs and promote safer driving practices. This ultimately leads to reduced accident risks and insurance costs.
Personal Vehicle Monitoring
GPS tracking systems can improve safety and security for personal vehicles. These systems offer peace of mind by providing location information and alerts in case of emergencies or unauthorized use. Furthermore, the data can be utilized for comprehensive driver behavior analysis.
- Enhanced Safety and Security: GPS tracking systems provide valuable information in case of emergencies or accidents. Knowing the exact location of a vehicle allows for quick response and assistance, improving safety outcomes. This technology also helps deter theft by providing proof of ownership and location.
- Driver Behavior Analysis: Data gathered from GPS tracking can reveal driving patterns, helping individuals identify areas for improvement in their driving habits. This includes information about speeding, braking patterns, and route choices. Analyzing this data can contribute to a more safety-conscious driving style and reduce risks.
Driver Behavior Analysis
GPS tracking data provides a wealth of information regarding driver behavior, contributing to a more safety-conscious environment and improved operational efficiency. This includes data about speed, acceleration, braking patterns, and idling time.
- Identifying Risky Driving Patterns: GPS tracking can identify and highlight instances of reckless driving, such as speeding, aggressive braking, or sharp turns. This data can then be used for driver training and education to mitigate these behaviors.
- Improving Driving Habits: By analyzing driver behavior, companies and individuals can identify areas where driving habits can be improved, promoting safer and more efficient driving practices. This can lead to a significant decrease in accidents and injuries.
- Evaluating Driver Performance: Data obtained from GPS tracking can be used to evaluate driver performance, identify high-performing drivers, and tailor training programs to address specific needs.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for ensuring the reliable operation of GPS trackers. Regular checks and prompt resolution of issues minimize downtime and maximize the value of the tracking system. A proactive approach to maintenance prevents potential problems and allows for swift action when malfunctions occur.Maintaining optimal performance of GPS trackers involves routine checks and updates, addressing common issues, and understanding how to handle malfunctions.
This ensures the continued accuracy and reliability of location data, allowing for effective fleet management and enhanced security.
Routine Checks and Updates
Regular inspections and software updates are essential for maintaining GPS tracker functionality. This proactive approach prevents potential problems and ensures the tracker remains in optimal working condition. It’s crucial to consistently monitor the battery life, signal strength, and physical condition of the tracker. Software updates, when available, should be applied promptly to incorporate bug fixes, performance enhancements, and new features.
- Inspect the tracker’s physical condition regularly for any signs of damage or wear. Look for cracks, dents, or corrosion.
- Check the battery level regularly to avoid unexpected power outages. A low battery level can hinder the tracker’s ability to maintain a GPS signal.
- Monitor the GPS signal strength, which impacts the accuracy of location data. A weak signal can lead to inaccuracies or lost tracking.
- Keep the software updated. Updates often include performance improvements, bug fixes, and new features, thereby ensuring the tracker’s reliability and effectiveness.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Addressing common GPS tracker problems effectively minimizes downtime and ensures smooth operation. A structured troubleshooting approach is key to quickly identifying and resolving issues.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| GPS signal loss | Obstructions (buildings, trees), weak signal, or device malfunction | 1. Move the tracker to an open area with clear visibility of the sky. 2. Check for any physical damage to the tracker. 3. Restart the device. 4. Update the tracker’s firmware if available. |
| Inaccurate location data | Signal interference, GPS signal blockage, or software issues | 1. Identify and remove any potential obstructions to the GPS signal. 2. Check for recent software updates and apply them. 3. Try a different location if possible to isolate the source of interference. 4. Contact support if the issue persists. |
| Battery drain | High power consumption, faulty battery, or software glitches | 1. Check the battery level and replace if necessary. 2. Restart the device. 3. Check for any running background applications consuming excessive power. 4. Review the power-saving features of the tracker’s software. |
Handling Malfunctions
Malfunctions in GPS trackers can be handled efficiently through a structured approach. This includes promptly diagnosing the issue and implementing the appropriate troubleshooting steps.
- When a malfunction occurs, immediately document the problem, including the date, time, and symptoms observed.
- Utilize the provided troubleshooting guide to identify possible causes and appropriate solutions.
- Contact technical support if the issue persists or if you lack the necessary tools or expertise to resolve it.
- In case of persistent malfunctions, consider replacing the GPS tracker if necessary.
Comparison of Different GPS Tracking Devices: GPS Tracker For Car
Choosing the right GPS tracking device for your car depends on various factors, including your budget, the level of detail you need, and the specific features required for your use case. This section delves into the diverse landscape of GPS trackers, comparing key specifications to help you make an informed decision.Different GPS tracking devices cater to various needs and budgets.
Understanding the features and capabilities of each type is essential for selecting the optimal solution.
Key Features Comparison
Various features differentiate GPS trackers, impacting their performance and overall utility. This comparison highlights key aspects for evaluation.
| Feature | Basic Tracker | Advanced Tracker | Premium Tracker |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location Accuracy | Sub-meter (depending on satellite visibility) | Meter-level accuracy, enhanced positioning | Centimeter-level accuracy, high-precision positioning |
| Battery Life | Typically 3-7 days | 7-14 days, or even longer with power-saving modes | Over 14 days, or even up to a month |
| Data Transmission | Cellular (2G/3G), potentially Wi-Fi | Cellular (4G/5G), GPS-enabled Wi-Fi or cellular data transmission | Cellular (4G/5G), satellite communication options for remote areas |
| Data Storage | Limited storage, often requires cloud subscription for longer-term data | Cloud storage, with options for local storage | Cloud storage with high data capacity, potential for offline data analysis |
| Additional Features | Basic location tracking | Speed monitoring, geofencing, alerts | Advanced analytics, remote diagnostics, vehicle health monitoring |
| Price | Low | Medium | High |
Analysis of Different GPS Tracking Solutions
Evaluating different GPS tracking solutions requires a thorough understanding of their strengths and weaknesses. This section provides a detailed comparison.
GPS trackers for cars are a great way to monitor vehicle location and potentially prevent theft. Pairing this with a solar-powered car charger, like the one detailed in Solar-powered car charger , could be a smart move for added convenience. Ultimately, a well-equipped GPS tracker, coupled with a reliable charging solution, is a worthwhile investment for any car owner.
- Basic Trackers: These are cost-effective options suitable for basic location tracking. They often rely on cellular networks for data transmission and have limited additional features. While their affordability is a major advantage, their limited features might not meet complex tracking needs. Example use case: Basic vehicle monitoring for occasional checks.
- Advanced Trackers: Offering more advanced features like speed monitoring, geofencing, and alerts, these devices cater to users requiring a higher level of detail. Their extended battery life and data transmission options provide a more reliable tracking experience compared to basic models. Example use case: Fleet management for delivery services needing precise tracking of vehicles.
- Premium Trackers: These are typically equipped with cutting-edge technology and advanced analytics. Their high accuracy and extensive data capabilities cater to users requiring detailed insights and monitoring. Example use case: Luxury vehicle owners or companies needing high-precision tracking and remote diagnostics for maintenance purposes.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a GPS Tracker
Several factors influence the selection of a GPS tracking device.
- Budget: Different devices come with varying price tags. Understanding your budget is crucial to narrowing down the options.
- Accuracy Requirements: The level of accuracy needed will depend on the specific application. Higher accuracy translates to a more precise tracking experience.
- Data Transmission Method: The reliability and coverage of the data transmission method are critical factors to consider. Cellular data is generally reliable but may be unavailable in remote areas. Satellite communication can provide an alternative but might come at a higher cost.
- Battery Life: Extended battery life is crucial for continuous tracking, reducing the need for frequent charging or replacements. This is especially important for fleet management or continuous monitoring scenarios.
- Additional Features: Features like geofencing, speed monitoring, or remote diagnostics enhance the device’s functionality, but these features may also increase the price.
Future Trends in GPS Tracking Technology
GPS tracking technology is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in sensor technology, artificial intelligence, and the increasing demand for precise location data. These advancements are reshaping the way we monitor and manage assets, vehicles, and even individuals, opening up exciting possibilities across various sectors. The future of GPS tracking promises even greater accuracy, enhanced capabilities, and integration with other emerging technologies.
Advanced Sensor Integration
The integration of advanced sensors with GPS tracking devices is a key trend. Beyond basic location data, these systems can now collect various environmental and operational parameters. For example, sensors can monitor vehicle speed, acceleration, engine temperature, fuel levels, and even driver behavior. This comprehensive data provides a more detailed understanding of vehicle performance and operational efficiency, enabling proactive maintenance and improved safety.
A GPS tracker for your car is a smart addition to enhance your vehicle’s safety. Completing this with an essential Emergency car safety kit provides a comprehensive safety solution. The tracker’s real-time location updates are incredibly valuable, especially in emergencies, and complement the comprehensive safety measures within the kit, ultimately boosting your car’s overall safety profile.
Real-time data from sensors can be used to identify potential issues and predict maintenance needs, ultimately lowering operational costs and preventing accidents.
AI-Powered Analysis
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly significant role in analyzing the massive datasets generated by GPS trackers. AI algorithms can identify patterns, anomalies, and trends in the data, enabling predictive maintenance, optimized routes, and improved security. For instance, AI can detect unusual driving patterns, potentially signaling driver fatigue or mechanical problems. Furthermore, AI-powered analysis can optimize delivery routes, minimizing fuel consumption and delivery times.
This data-driven approach is revolutionizing logistics and transportation management.
Evolution of GPS Tracking in Future Transportation
GPS tracking is set to become an integral component of future transportation systems. The integration of GPS with autonomous vehicles will be critical for navigation, localization, and safety. Autonomous vehicles rely on precise location data for safe and efficient operation, making GPS trackers an essential element for the success of this technology. Moreover, advancements in connected car technology will facilitate seamless integration of GPS data with other systems, enhancing vehicle performance and safety.
The future of transportation will rely on accurate and real-time location data, as autonomous vehicles become more prevalent.
Potential Future Uses in Autonomous Vehicles
GPS trackers will play a crucial role in the development and deployment of autonomous vehicles. Precise location data is vital for navigation, localization, and collision avoidance. GPS tracking systems will also help in monitoring the performance of autonomous vehicles, providing data on driving patterns, environmental factors, and safety measures. Further, these systems can be used to manage fleets of autonomous vehicles, ensuring efficient routing and optimized operations.
GPS tracking systems will be fundamental for the safe and reliable operation of autonomous vehicles in the future.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, GPS trackers for cars offer a multitude of benefits, ranging from enhanced security and safety to improved operational efficiency. This comprehensive guide has explored the various facets of GPS car tracking, equipping readers with the knowledge to make informed decisions. From detailed features and functionalities to considerations around security and privacy, this guide serves as a valuable resource for anyone looking to utilize this technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the typical costs for GPS trackers for cars?
GPS tracker prices vary greatly depending on features, quality, and functionality. Basic models start at a few hundred dollars, while more advanced units with additional sensors or data analytics capabilities can cost several thousand dollars.
How accurate is GPS tracking in urban areas with many tall buildings?
GPS accuracy can be affected by factors like dense urban environments and tall buildings that can block satellite signals. While the technology is generally accurate, users should be aware of potential inaccuracies, particularly in highly-built-up areas.
What are some common troubleshooting steps for GPS tracker malfunctions?
Common troubleshooting steps include checking the power supply, ensuring proper installation, and confirming a clear signal. If the problem persists, contacting the manufacturer’s support or a qualified technician is recommended.
What are the legal implications of using GPS trackers in different regions?
Legal regulations regarding GPS tracking vary by region and country. It is crucial to research and understand the local laws and regulations before implementing GPS tracking systems, especially for business or commercial use.