EV charging regulations are rapidly evolving globally, shaping the future of electric vehicle adoption. This comprehensive overview explores the diverse landscape of charging infrastructure, from Level 1 to Level 3, and the national and regional policies influencing their deployment. Key factors driving these regulations are also examined, highlighting the interconnectedness of charging standards, safety protocols, and environmental considerations.
Different countries and regions have varying standards for EV charging, impacting interoperability. Understanding these differences is crucial for seamless charging experiences and fostering a global EV ecosystem. This discussion will cover public and residential charging regulations, including permitting, installation requirements, and grid integration strategies.
Introduction to EV Charging Regulations
The global landscape of electric vehicle (EV) charging is rapidly evolving, driven by increasing adoption of EVs and the need for robust infrastructure. This evolution necessitates clear and comprehensive regulations to ensure safety, interoperability, and equitable access to charging facilities. These regulations are multifaceted, encompassing everything from the types of charging stations to the policies governing their deployment and operation.The development of EV charging regulations is a dynamic process, reflecting a complex interplay of technological advancements, environmental concerns, and economic considerations.
Various national and regional authorities are actively shaping the future of EV charging through a range of policies, influencing the overall accessibility and usability of electric vehicle charging networks.
Different Types of EV Charging Infrastructure
EV charging infrastructure is categorized into three levels based on power output and associated charging time. Understanding these levels is crucial for comprehending the regulatory frameworks governing EV charging.
- Level 1 Charging: This basic charging method utilizes standard household power outlets, resulting in extremely slow charging rates. While suitable for occasional top-ups, it is generally insufficient for daily commutes or longer journeys.
- Level 2 Charging: This intermediate charging option utilizes dedicated 240-volt outlets, significantly increasing charging speeds compared to Level 1. Level 2 chargers are commonly found in residential and public settings and are often integrated with advanced features like smart charging capabilities and monitoring systems.
- Level 3 Charging: Also known as DC Fast Charging, Level 3 offers the fastest charging speeds, enabling significant battery replenishment in a relatively short time. These high-powered chargers are strategically positioned along major highways and public areas to cater to the needs of long-distance EV travelers.
National and Regional Policies Impacting EV Charging
Various national and regional governments have implemented policies to stimulate the deployment of EV charging infrastructure. These policies vary significantly in their scope, focus, and incentives.
- Mandates and Incentives: Many jurisdictions mandate the installation of EV charging stations in public areas, and offer incentives like tax credits or subsidies to encourage private sector participation. These mandates often come with detailed specifications regarding charger types, accessibility, and maintenance.
- Grid Infrastructure Considerations: The integration of EV charging into existing electricity grids is crucial, and many regions are developing regulations to ensure grid stability and manage the surge in electricity demand during peak charging periods. This often involves planning for smart charging strategies and network upgrades.
- Examples of Policies: The EU’s commitment to a large-scale EV charging network deployment, or specific state incentives for the installation of EV charging stations at public parking facilities, illustrate the varying approaches to EV charging infrastructure development. These initiatives often emphasize strategic placement of charging stations, ensuring sufficient coverage to facilitate EV adoption.
Key Factors Driving EV Charging Regulations
Several key factors are driving the development and evolution of EV charging regulations.
- Growing EV Adoption: The rising popularity of electric vehicles necessitates the creation of a supportive charging infrastructure to accommodate the increased demand.
- Environmental Concerns: Regulations are often shaped by the need to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable transportation solutions.
- Technological Advancements: New charging technologies and standards influence the development of regulatory frameworks, ensuring interoperability and efficiency.
Charging Infrastructure Standards
Different countries and regions are adopting various charging standards for electric vehicles (EVs). This necessitates a robust understanding of these standards to ensure interoperability and facilitate seamless EV charging experiences. Harmonization of these standards is crucial for the widespread adoption of EVs.
Comparison of Charging Standards
A variety of charging standards exist globally, each with its own voltage, amperage, and connector type. This diversity presents challenges in ensuring that EV chargers are compatible across different regions. The table below illustrates the varying standards employed by different countries or regions:
| Region/Country | Voltage (V) | Amperage (A) | Connector Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America (USA, Canada) | 240 | 16-48 | J1772 |
| Europe (many countries) | 230 | 16-22 | Type 2 |
| China | 220 | 16-120 | CCS Combo 2 |
| Japan | 100 | 16 | CHAdeMO |
Implications of Varying Standards on Interoperability
The differences in charging standards across countries and regions pose significant challenges for EV charger interoperability. Drivers may encounter issues when trying to charge their EVs in different countries due to incompatibility between charging connectors. For instance, an EV with a Type 2 connector would not be able to charge at a station equipped with a J1772 connector without an adapter.
This lack of standardization creates a significant hurdle for widespread EV adoption. Furthermore, the varying voltage and amperage specifications add complexity to the charging process.
Role of Standardization Bodies
Standardization bodies play a critical role in shaping EV charging regulations. These organizations establish technical specifications and guidelines that dictate the design and implementation of EV charging infrastructure. Examples of these standardization bodies include the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). These bodies ensure that EV charging standards are technically sound and meet the needs of various stakeholders.
Typical Installation Requirements for Public EV Charging Stations
Establishing public EV charging stations necessitates adherence to specific installation requirements. These requirements are primarily concerned with electrical safety and accessibility.
- Electrical Safety Standards: Compliance with electrical safety codes is paramount to prevent accidents. This includes the use of appropriate wiring, grounding, and circuit breakers. The installation should meet the standards set by local electrical codes, ensuring safety measures are implemented. This is critical for preventing fire hazards or electrical shocks.
- Accessibility Standards: EV charging stations should be designed to accommodate people with disabilities. This includes considerations for wheelchair accessibility, visual aids, and other accessibility features. Compliance with accessibility standards ensures that charging stations are inclusive for all users. The inclusion of features such as ramps, designated parking spaces, and accessible entrances is essential for meeting accessibility standards.
Public Charging Station Regulations
Public charging stations are crucial for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Clear regulations ensure the safe, efficient, and equitable provision of these services to the public. These regulations cover various aspects, from permitting and licensing to maintenance and location considerations.Regulations for public EV charging stations are designed to manage the rapid expansion of charging infrastructure. They aim to prevent haphazard installations, prioritize safety, and ensure accessibility for all users.
Furthermore, these regulations often consider environmental impacts and integrate with existing infrastructure.
Permitting and Licensing Processes
The permitting and licensing process for installing public EV charging stations varies by jurisdiction. Generally, applicants must submit detailed plans outlining the location, technical specifications, and safety measures for the proposed charging station. These plans are reviewed by relevant authorities, including environmental agencies, transportation departments, and utility companies. Approval hinges on compliance with local ordinances and safety standards.
Permitting timelines can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the project and the specific regulations of the jurisdiction.
Location Selection and Accessibility
Strategic location selection is vital for the success of public charging stations. Regulations typically prioritize areas with high vehicle traffic, convenient access points, and adequate parking. These criteria often consider the density of residential areas, proximity to businesses, and public transportation hubs. Accessibility standards are paramount, ensuring the charging stations are readily available to individuals with disabilities.
Clear signage and sufficient space around the stations are also crucial. Regulations may include specific requirements for ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) compliance.
Charging Station Maintenance and Safety Protocols
Maintenance and safety are critical aspects of public EV charging station operations. Regulations typically mandate regular inspections, maintenance schedules, and reporting requirements for malfunctions or safety issues. These regulations address the electrical safety of the equipment, ensuring compliance with national and local electrical codes. Maintenance protocols may also include provisions for timely repairs, replacement of faulty components, and emergency response procedures.
This prioritizes the safety of users and the reliability of the charging infrastructure. Regulations often require the installation of safety features like ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) to prevent electrical hazards.
Impact on Public Areas
Regulations significantly impact the provision of charging services in various public areas. For example, in parking lots, regulations dictate the number of charging stations allowed, their placement relative to other parking spaces, and the availability of dedicated parking areas for EVs. On highways, regulations often focus on the location and accessibility of charging stations along routes, factoring in travel time and anticipated traffic patterns.
The regulations aim to balance the needs of EV drivers with the existing infrastructure and traffic flow of public areas. These rules often consider the aesthetics and design of the charging stations, ensuring they blend seamlessly with the surrounding environment. Furthermore, the integration of charging stations with existing infrastructure may require specific regulations regarding utility connections and grid capacity.
Residential Charging Regulations: EV Charging Regulations
Residential EV charging regulations are evolving rapidly to accommodate the growing adoption of electric vehicles. These regulations encompass a range of factors, from permitting processes to electrical grid upgrades, aiming to ensure a seamless and sustainable transition to electric mobility. The specifics vary significantly between countries, reflecting diverse energy policies and infrastructure development stages.Residential charging regulations are crucial for facilitating widespread EV adoption.
Clear guidelines for installation, permitting, and grid integration are essential for both consumers and utility companies. A well-structured regulatory framework encourages responsible charging practices, minimizes grid strain, and ensures the safety and reliability of the charging infrastructure.
Permitting Processes for Residential Charging
Different jurisdictions have varying permitting requirements for residential EV chargers. Some countries have streamlined permitting processes for standard installations, while others require more extensive documentation and inspections. This can include submitting plans for electrical work, obtaining building permits, and adhering to local codes and ordinances. These regulations ensure that installations meet safety standards and comply with local regulations.
Installation Requirements for Residential EV Chargers
Residential EV charging installations must adhere to specific safety and performance standards. These requirements vary by location and are typically Artikeld in national or regional electrical codes. They often dictate the type of wiring, circuit breakers, grounding systems, and the location of the charging station within the property. Strict adherence to these standards is critical to prevent electrical hazards and ensure the safety of homeowners and neighbors.
Electrical Grid Upgrades and Residential EV Charging
The integration of residential EV charging infrastructure can place a significant strain on local electrical grids. Some jurisdictions are implementing regulations that require grid upgrades to handle the increased demand, especially in areas with high EV adoption rates. This could involve strengthening power lines, installing new transformers, or upgrading existing infrastructure. Regulations often mandate that homeowners or utility companies undertake these upgrades, based on the local energy grid capacity.
For example, in areas experiencing significant EV adoption, utility companies might require new power lines to handle the increased demand.
Role of Utility Companies in Residential EV Charging Regulations
Utility companies play a crucial role in the development and implementation of residential EV charging regulations. They often provide guidance on grid capacity and suggest suitable charging solutions. Utility companies might also participate in developing incentives and programs to encourage EV adoption. Their expertise in managing electricity grids is invaluable in ensuring that the integration of residential charging stations is smooth and sustainable.
Incentives and Subsidies for Residential EV Charging Infrastructure
Many governments offer incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of residential EV charging infrastructure. These incentives can take various forms, such as rebates for the purchase and installation of chargers, tax credits, or grants. These incentives are crucial to reduce the upfront cost of EV charging and encourage wider adoption. For example, some regions offer rebates for installing Level 2 EV chargers, which are more common for residential use.
Regulations for Charging Station Placement within Residential Properties
Regulations governing the placement of charging stations within residential properties address factors such as safety, accessibility, and aesthetics. These regulations often include guidelines on the distance from flammable materials, the placement in relation to other building structures, and considerations for aesthetics. Clear guidelines are important to avoid potential hazards and maintain the visual appeal of the property. For instance, regulations may prohibit installing chargers near gas tanks or in areas where they could impede pedestrian traffic.
Grid Integration and Energy Management
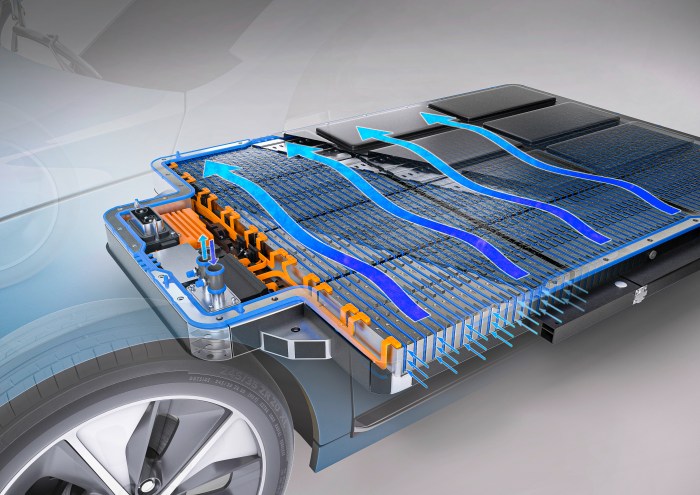
EV charging regulations play a crucial role in ensuring the seamless integration of electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure into existing power grids. Proper planning and implementation of these regulations are essential to maintain grid stability and capacity, preventing potential disruptions to the overall energy system. Strategies for optimizing integration and managing charging loads are vital for the widespread adoption of EVs.Successfully integrating EV charging into the electrical grid requires careful consideration of various factors.
These include the fluctuating nature of charging demand, the potential for overloading existing infrastructure, and the need to balance charging needs with other electricity demands. Regulations need to account for these variables, providing a framework for sustainable and reliable energy provision.
Impact on Grid Capacity and Stability
EV charging significantly impacts the electrical grid’s capacity and stability. Large-scale EV charging can lead to substantial increases in peak demand, potentially exceeding the grid’s capacity, causing voltage fluctuations, and affecting the stability of the power supply. This necessitates proactive planning and regulation to mitigate potential issues.
Strategies for Optimizing Grid Integration
Several strategies can optimize the integration of EV charging infrastructure into existing power grids. These include advanced grid planning tools, which forecast and model future demand to ensure sufficient capacity. Smart grid technologies, such as advanced metering infrastructure, provide real-time data to better manage charging loads and prevent grid overload. Smart charging protocols and communication protocols also play a vital role in controlling charging rates and coordinating charging sessions to reduce peak demands.
Regulations for Demand Response Programs
Demand response programs are essential for managing peak charging loads. These programs incentivize EV drivers to shift their charging to off-peak hours, thereby reducing the strain on the grid during peak periods. Regulations can include time-of-use pricing structures, offering incentives for charging during off-peak hours, and penalties for charging during peak hours. These measures encourage responsible charging practices and help balance the load on the electrical grid.
Role of Smart Charging Technologies
Smart charging technologies play a vital role in mitigating grid stress. These technologies dynamically adjust charging rates based on real-time grid conditions, ensuring that charging does not exceed available capacity. Smart charging systems can communicate with the grid, enabling them to optimize charging schedules and reduce peak demand. These systems can also utilize real-time pricing signals to adjust charging speeds based on electricity prices, further reducing peak load demand.
For example, some smart charging systems can communicate with the grid, allowing it to predict charging demand and adjust the power distribution accordingly. This proactive approach helps prevent grid overload and maintains system stability.
Environmental Regulations and EV Charging
Environmental regulations are increasingly crucial in shaping the development of electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure. These regulations are vital for mitigating the environmental impact of this expanding sector, encompassing considerations for emissions, waste management, and the integration of renewable energy sources. A holistic approach is needed to ensure sustainable transportation practices.
Influence of Environmental Regulations on EV Charging Infrastructure
Environmental regulations play a significant role in driving the development of EV charging infrastructure. Stringent regulations on emissions, waste disposal, and energy sourcing compel the industry to adopt cleaner practices. For instance, regulations requiring the use of renewable energy for charging stations incentivize the integration of solar panels and wind turbines into charging infrastructure. These regulations not only promote sustainable practices but also ensure compliance with environmental standards.
Environmental Impact Regulations for Charging Stations
Regulations concerning the environmental impact of charging stations are essential to minimize their footprint. These regulations address factors such as emissions, noise pollution, and waste management. Stricter guidelines on noise levels for charging equipment and waste disposal procedures for batteries and components are common elements. Furthermore, regulations often mandate the use of environmentally friendly materials in construction and the implementation of effective waste management systems to handle battery disposal, promoting responsible e-waste management.
Role of Renewable Energy Sources in EV Charging
Renewable energy sources are pivotal in the context of EV charging. The integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into charging stations is increasingly mandated by environmental regulations. This approach reduces reliance on fossil fuels and decreases the carbon footprint of EV charging. For example, several countries are implementing policies that require a specific percentage of electricity used for EV charging to originate from renewable sources.
This creates a demand for renewable energy generation, stimulating investment in solar and wind farms.
Promotion of Sustainable Transportation Practices through EV Charging Regulations
EV charging regulations play a critical role in fostering sustainable transportation practices. By mandating the use of renewable energy and promoting efficient charging infrastructure, these regulations accelerate the transition to a greener transportation system. Regulations encouraging the use of electric vehicles and implementing incentives for adopting them contribute to reduced emissions and improved air quality. Furthermore, policies that incentivize the development of smart charging systems, optimizing energy consumption, contribute to sustainability.
Safety and Security Regulations
Robust safety and security measures are paramount for EV charging infrastructure. These regulations are crucial for protecting users, ensuring the reliability of the system, and mitigating potential risks associated with electrical components, vandalism, and accidents. Compliance with these standards fosters public trust and encourages wider adoption of electric vehicles.Effective safety protocols and security measures are vital for the safe and reliable operation of EV charging stations.
These regulations encompass a range of aspects, from electrical safety and fire prevention to data protection and emergency response procedures. Comprehensive adherence to these regulations safeguards users, protects infrastructure, and contributes to the overall success of the EV charging ecosystem.
Electrical Safety Standards, EV charging regulations
Ensuring the electrical safety of EV charging stations is paramount. This involves strict adherence to national and international electrical safety codes and standards. These standards address the use of appropriate wiring, grounding, and surge protection. Properly sized and installed circuit breakers and fuses are critical to prevent electrical overloads and fires. Regular inspections and maintenance of electrical components are essential to identify and address potential hazards.
This includes checking connections, insulation, and the condition of wiring and conduit. Testing and verification procedures must be rigorously implemented to guarantee the safety of the system.
Fire Prevention Measures
Fire prevention measures are crucial for EV charging stations to mitigate risks associated with electrical faults, battery overheating, and other potential hazards. This involves the use of fire-resistant materials in construction, automatic fire suppression systems, and clearly marked emergency exits. Properly maintained and regularly inspected fire suppression systems are critical to effectively contain and extinguish fires. Regular training for station personnel on fire safety procedures is essential to ensure a prompt and effective response in the event of a fire.
Equipment Maintenance Protocols
Regular equipment maintenance is essential to prevent malfunctions and ensure the reliability of EV charging stations. This includes routine inspections of charging equipment, electrical components, and safety systems. Maintenance schedules should be developed and followed to prevent potential hazards. Equipment manufacturers’ guidelines should be strictly adhered to. Any maintenance work should be carried out by qualified personnel, ensuring that all safety procedures are followed.
Logging and documenting maintenance activities is crucial for tracking the history of the equipment and for identifying potential trends or patterns.
Security Measures Against Vandalism and Theft
Security measures are essential to protect EV charging stations from vandalism and theft. These measures include installing robust security systems, such as surveillance cameras, access control systems, and perimeter fencing. The use of high-quality materials and robust construction can deter unauthorized access. Lighting can be installed to improve visibility and deter criminal activity. Regular security audits are important to evaluate the effectiveness of the implemented measures and identify vulnerabilities.
Working with local law enforcement agencies to address any reported incidents or potential threats is crucial.
Data Privacy and Security Regulations
Data privacy and security regulations are critical for EV charging users. Regulations should ensure that personal data collected by charging stations is handled responsibly and securely. This involves establishing clear data handling policies, encryption of sensitive information, and secure storage of user data. Compliance with data protection laws and standards is paramount. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are important to ensure that data is protected against unauthorized access, breaches, or misuse.
EV charging regulations are becoming increasingly complex, mirroring the evolving landscape of transportation. The need for consistent standards is clear, but consideration must also be given to the legacy of car exhaust systems, car exhaust systems and their impact on air quality. Ultimately, effective EV charging regulations need to balance environmental goals with practical considerations for infrastructure and public use.
Transparency about data collection and usage practices is crucial for building trust.
Regulations for Charging Accidents and Emergencies
Regulations for handling potential charging accidents and emergencies are critical. Emergency response plans should be in place, including procedures for responding to incidents such as fires, electrical shocks, and equipment malfunctions. These plans should clearly define roles and responsibilities for station personnel and emergency services. Emergency contacts and procedures for notifying relevant authorities should be clearly communicated.
Training programs for station personnel on emergency procedures are critical to ensure a prompt and effective response in the event of an emergency. Regular drills and simulations are beneficial to practice and improve emergency response protocols.
Accessibility and Inclusivity Regulations
Regulations promoting accessibility and inclusivity for EV charging stations are crucial for ensuring equitable access to electric vehicle technology. These regulations address the needs of diverse user groups, fostering a more inclusive and equitable transition to electric mobility. These considerations extend beyond simply providing charging points; they involve designing systems that are usable and practical for all.EV charging infrastructure must be accessible to individuals with disabilities, ensuring compliance with relevant accessibility standards.
EV charging regulations are becoming increasingly complex, impacting not only the infrastructure but also the overall cost of ownership. Factors like location-specific fees and varying charging station pricing models can significantly affect your monthly car payments, impacting the long-term financial picture. Understanding these regulations is crucial for anyone considering an electric vehicle, as they directly influence the practicality and affordability of EV ownership.
This involves accommodating a range of mobility limitations and technological requirements, creating a truly inclusive experience for all.
Physical Accessibility Considerations
Regulations mandate the physical accessibility of EV charging stations, considering various disabilities. These include provisions for ramps, appropriate widths of walkways, designated parking spaces, and tactile paving for visual impairments. Specific requirements for accessible charging stations may include lowered charging ports for wheelchair users, ensuring appropriate spacing around the station for mobility aids, and provision of ample maneuvering space.
These features should be incorporated in the design phase of charging station construction, minimizing retrofitting needs and maximizing functionality.
Technological Accessibility Considerations
Technological accessibility plays a vital role in ensuring all users can effectively utilize EV charging stations. This includes provisions for clear and accessible signage in multiple languages and formats, with consideration for individuals with visual impairments. Audio cues, text-to-speech capabilities, and alternative communication methods for individuals with hearing impairments are also crucial. Smart charging systems and mobile apps should offer various options for payment and communication, including accessible interfaces for individuals with dexterity limitations.
Charging Stations for People with Disabilities
Dedicated charging stations for individuals with disabilities are essential. These may be located in designated areas, offering ample space for maneuvering and providing clear signage to indicate accessibility. These dedicated spaces should include ramps and other mobility aids for easier access. Specific design features should consider wheelchair accessibility, ensuring charging ports are easily accessible and compliant with relevant standards.
Examples of dedicated spaces might include designated parking areas with charging stations close by.
Diverse Charging Solutions
Diverse charging solutions cater to varying needs and preferences. Different charging speeds, from Level 1 to Level 3, cater to various needs. This flexibility enables different users to choose charging options that meet their requirements. Faster charging options are crucial for businesses and frequent travelers, while slower charging options may be preferred for residential users. The availability of different charging solutions is vital for fostering a comprehensive and equitable charging infrastructure.
Public Charging Station Requirements
EV charging stations in public spaces should adhere to strict accessibility guidelines. Regulations may dictate minimum distances between charging stations and accessible amenities, ensuring ease of access for all users. These stations should be strategically placed in public areas, providing convenient access to amenities and ensuring safety and security. The design should consider the surrounding environment and minimize potential hazards.
For example, stations should be located away from busy pedestrian areas to prevent congestion and accidents. Public charging stations should also provide clear signage, including accessibility information.
Financial Regulations and Incentives

Financial regulations and incentives play a crucial role in driving the adoption and expansion of electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure. These regulations create a supportive environment for investment in charging technology, encouraging the development of a robust network of charging stations. By offering financial support, governments aim to reduce barriers to entry for private companies and public entities, thus accelerating the transition to a sustainable transportation system.
Financial Incentives for Charging Infrastructure Development
Financial incentives, such as tax credits and subsidies, are often provided to encourage the installation of EV charging stations. These incentives are designed to reduce the financial burden associated with setting up charging infrastructure, thereby increasing the profitability of investments and making it more attractive to private companies and public bodies to invest in the technology.
- Tax Credits: Tax credits are a common incentive offered to businesses and individuals for the installation of EV charging stations. These credits often reduce the tax burden on investments in charging infrastructure, making it a more attractive option financially. For example, a company might see a significant reduction in their tax liability for investing in charging stations, making the project more financially feasible.
- Government Grants: Government grants are another crucial financial support mechanism. These grants can be provided for various stages of charging station deployment, from design and planning to construction and operation. This funding can cover a significant portion of the project’s cost, making the venture more accessible and profitable.
- Rebates: Rebates are frequently offered for purchasing and installing EV charging equipment. These rebates directly reduce the cost of the equipment, encouraging greater adoption of EV charging stations, particularly in residential areas. Rebates are typically calculated based on the cost of the equipment, with a fixed percentage or an amount as a rebate.
Regulations on Charging Tariffs and Pricing Models
Establishing clear and transparent regulations for charging tariffs and pricing models is essential for maintaining fair competition and consumer confidence. These regulations aim to prevent exploitation and ensure that consumers are not unfairly burdened by exorbitant costs.
- Open Access Standards: Regulations might mandate open access standards for charging networks. This ensures that various charging providers can access and use the charging infrastructure, promoting competition and offering consumers a wider range of options in terms of pricing and services.
- Time-of-Use Tariffs: Regulations can also promote time-of-use tariffs for charging, encouraging off-peak charging. This approach balances demand on the electrical grid, reduces costs for consumers, and minimizes the strain on electricity supply during peak hours. The implementation of such tariffs could be a step toward sustainable energy consumption.
- Transparency and Pricing Models: Regulations regarding the pricing structure for charging must be transparent and readily available to the consumer. This will foster trust and ensure that consumers are fully aware of the costs associated with using the charging station.
Examples of Financial Support Mechanisms
Various jurisdictions have implemented financial support mechanisms to incentivize EV charging infrastructure development. These mechanisms vary in their design and scope, but their common objective is to reduce the financial burden on investors and accelerate the deployment of charging stations.
- California: California offers various financial incentives, including tax credits and grants, to support the installation of EV charging stations. These incentives are designed to reduce the cost of setting up charging stations and make it more attractive for businesses and individuals to invest in the technology.
- Germany: Germany has a comprehensive support scheme, including tax incentives and grants, for the installation of charging stations. The scheme aims to promote the widespread adoption of EVs and the development of a robust charging network across the country.
International Collaboration and Harmonization
Establishing uniform EV charging regulations across international borders presents significant challenges, but also substantial opportunities. The varying national priorities and infrastructural landscapes necessitate a collaborative approach to ensure seamless EV adoption and market growth. This necessitates coordinated efforts to create a global standard for EV charging infrastructure, potentially leveraging existing agreements and protocols to facilitate this standardization.
Challenges and Opportunities of International Collaboration
International collaboration in establishing EV charging regulations faces challenges due to differing national priorities, regulations, and technical standards. These variations can hinder the development of a consistent charging infrastructure across borders. However, the opportunities are considerable. Harmonized regulations can lead to increased EV adoption rates, stimulate market growth, and reduce consumer confusion. A unified approach will encourage cross-border travel and facilitate the integration of charging networks.
Key Stakeholders in International Harmonization Efforts
Several key stakeholders play critical roles in international harmonization efforts. These include governments, automotive manufacturers, charging infrastructure providers, energy companies, and standardization organizations. Collaboration among these diverse groups is essential for the successful implementation of uniform regulations. International bodies, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), also play a pivotal role in developing and promoting global standards.
Benefits of Harmonized Regulations for EV Adoption and Market Growth
Harmonized EV charging regulations provide numerous benefits for EV adoption and market growth. A standardized approach fosters a more predictable and reliable charging experience for drivers, encouraging wider adoption. This consistency across borders simplifies the process of charging for travelers and enhances the overall appeal of EVs. Furthermore, harmonized regulations stimulate market growth by reducing barriers to entry for charging infrastructure providers and promoting investment in EV technology.
Existing International Agreements Related to EV Charging
Several international agreements and initiatives exist, although not specifically focused solely on EV charging regulations. These often encompass broader energy policies and sustainability initiatives. Some examples include agreements on mutual recognition of vehicle emissions standards and cooperation on renewable energy development. While not explicitly dedicated to EV charging, these frameworks lay the groundwork for future collaborations in this sector.
The absence of a dedicated global agreement highlights the need for dedicated international discussions and agreements to effectively address EV charging regulations.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, EV charging regulations are a complex interplay of technological, environmental, and economic factors. Harmonizing these regulations globally is essential for widespread EV adoption. The discussion highlighted the diverse facets of this critical infrastructure, from safety and accessibility standards to financial incentives and international collaboration. Addressing the challenges and leveraging the opportunities presented by these regulations is paramount to achieving a sustainable and inclusive electric transportation future.
User Queries
What are the typical installation requirements for public EV charging stations?
Typical installation requirements for public EV charging stations include adherence to electrical safety and accessibility standards, detailed in specific national or regional codes. These standards usually specify the required electrical infrastructure, grounding, and protective measures, as well as accessibility features for users with disabilities. Specific requirements vary significantly based on local building codes and regulations.
What incentives and subsidies are available for residential EV charging infrastructure?
Various countries and regions offer incentives and subsidies for installing residential EV charging infrastructure, such as tax credits, rebates, and grants. These incentives aim to promote EV adoption by reducing the upfront costs for homeowners. The specific types and amounts of incentives vary by location and are often tied to specific charging technologies or charging station types.
How do environmental regulations influence the development of EV charging infrastructure?
Environmental regulations play a significant role in shaping the development of EV charging infrastructure, emphasizing the need for sustainable practices. Regulations may focus on the environmental impact of charging stations, such as emissions and waste management. They may also promote the use of renewable energy sources for EV charging.
What are the key factors driving the development of EV charging regulations?
Key factors driving the development of EV charging regulations include the need to ensure safety and reliability of charging infrastructure, promote interoperability and standardization of charging stations, manage grid integration and energy consumption, and foster sustainable transportation practices.





